Cybersecurity and data breach incidents have become very common today in all the industries, especially healthcare.
Every now and then, a new data breach story about healthcare sector gains traction, exposing the personal and confidential data and information of the patients.
To ensure privacy and security of health data, the Indian government is bringing a new healthcare data protection law— Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA).
What is Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA) in India?
In November 2017, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW), Government of India, issued a draft to bring a healthcare security law in India. Called DISHA, the new law will soon become effective in the country.
Once effective, it will standardize and control the processes of collecting, storing, sharing, and using the digital health data. This standardization will help in ensuring that digital health data remains private, confidential, and secure.
Why secure digital health data?
Digital health data is actually the information about an individual in an electronic form. This data can be the information:
- related to physical or mental health;
- related to health service provided to the individual;
- about an organ or blood donated by the individual;
- found from examining a body part;
- related to a clinical establishment used by the individual.
All the digital health-related information is sensitive because if it gets compromised, lost, or exposed, it can be used to cause harm, violence, discrimination, and embarrassment to the individuals.
It can be used illegally or by unauthorized entities to judge and make decisions about the physical and mental conditions, sexual orientation, alcohol consumption, HIV status, abortion, etc.
Hence, the Indian government wants to ensure that all the digital health data of consumers in India remains secure and private.
Read details in a report by Forrester.
What is the purpose of DISHA healthcare act?
The purpose of DISHA healthcare act is to enable the secure exchange of health information of individuals between hospitals and clinics, and vice versa.
It will help in maintaining the privacy, confidentiality, and security of electronic health data, and in regulating the storage and exchange of electronic health records.

The DISHA healthcare law will give complete control of digital health data to the owner of that data. The owner of digital health data will have the right to:
- allow or refuse the clinical entities to generate and collect his/her data;
- refuse, allow, or withdraw his/her consent for storing and sharing of data;
- refuse entities from accessing or exposing his/her data;
- choose what should be collected and whatnot, based on the purpose of data;
- know where the data is being transmitted and to whom;
- access his/her data;
- get his/her health information rectified by the related entity if there is any inaccuracy or incomplete data;
- get notification by the related entity whenever a clinical establishment accesses the data;
- if there is any health emergency, the data will be shared with family members;
- get compensation if any damage is caused because of a data breach.
Does India really need a healthcare data security law?
Among the countries affected by cyberattacks, India ranks second. Recently, the US-based cybersecurity firm FireEye reported that attackers from China compromised an Indian healthcare website and breached more than 68 lakh health records which contained information of patients and doctors.
These attackers then directly sold the stolen information in underground forums. How do the cybercriminals benefit from digital health data?
According to FireEye, the average cost of a single stolen record in healthcare is $380, which is the highest among all the industries.
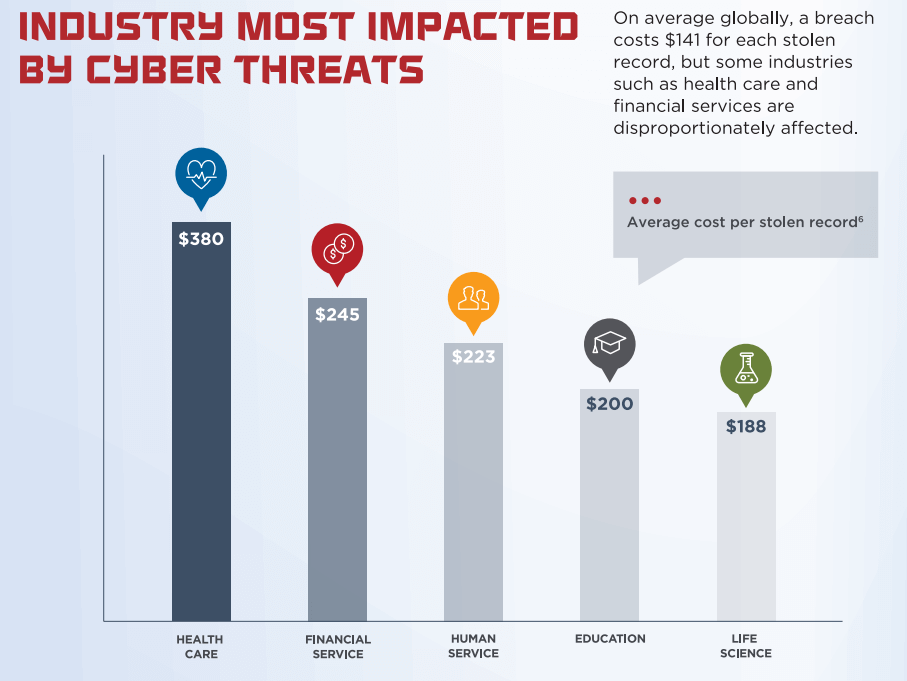
After carrying out a successful cyberattack on healthcare websites or organizations, attackers breach the health data and sell it in the black market. This stolen data can be used for ill purposes.
“The sheer number of healthcare-associated databases for sale in the underground is outrageous. Even more concerning, many of these databases can be purchased for under $2,000.” – FireEye
These stats and consequences of stolen health data show that India really needs a healthcare data protection law.
Duties of healthcare organizations under Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA)
Once the DISHA data protection law comes into effect, the healthcare organizations will need to comply with it at the earliest. Under DISHA, the healthcare sector in India will need to:
- inform the owner before collecting his/her digital health data;
- tell the owner about the purpose of data collection;
- inform the owner about the entities with whom the data is being shared, within three working days;
- share identity of the people who can access the data;
- hold and store the digital health data of individuals on behalf of the National Electronic Health Authority.

Apart from these, the healthcare industry in India will have to strictly take care that all the digital records remain private, confidential, and secure.
Following are the main measures that will need to be taken care of:
- Data encryption
If the digital health data is being shared or transmitted to health information exchange or other healthcare organizations, then this will need to be done in an encrypted form. What encryption does is protect the data from being compromised while it reaches from one entity to another.
- Data security
To ensure the privacy, confidentiality, and security of digital health data, the healthcare industry in India will have to implement all the necessary physical, administrative, and technical measures.
For instance, they will need to use modern data security and cloud backup solutions like Acronis Cloud Backup that can provide protection against ransomware, back up data to the cloud in an encrypted manner and keep everything private.
Related read: Why data security is the biggest concern of healthcare and how to fix it?
- Training
Organizations in healthcare will have to conduct regular trainings for their personnel so that they can maintain compliance with the security protocols mentioned in India’s data protection law.
What if healthcare organizations in India don’t comply with DISHA act?
Generally, the significance of any law is measured on the basis of the consequences that would follow if the law is not taken seriously. The same thing is also applicable to DISHA.
Following are the consequences that will follow if healthcare organizations in India don’t comply with DISHA act:
- Failure in compliance
If an entity or organization does not comply with the DISHA healthcare act, it will be fined with a penalty of minimum ₹1 lakh. ₹10,000 will be additional fine for each day till the failure in compliance continues, to a maximum of ₹1 crore.
- Breach of digital health data
If an entity collects, stores, and discloses the digital health data, or not secure the data per the standards, or damages, destroys, deletes, tamper with data, then the entity will have to compensate and pay for the damages to the owner of data.
- A serious breach of digital health data
If a person breaches the data dishonestly/ intentionally/ fraudulently, or if the person fails to secure the data in accordance with the DISHA act, or uses the data for commercial purposes, or commits the breach repeatedly, then the person or entity will be punished with imprisonment of 3-5 years or fine of more than ₹5 lakh.
How to ensure healthcare data security in India?
In order to avoid penalties from the Indian government and maintain the reputation of a secure healthcare organization, you must adopt a modern cloud backup and data security solution like Acronis Cloud Backup that comes powered by artificial intelligence (AI). It can protect your data against all the major attacks like ransomware and malware.

To know more about Acronis, talk to our cybersecurity consultants or book a free demo today.
Also, let us know your thoughts or queries about DISHA healthcare act.
Read details in a report by IDC.



